Acute flaccid myelitis
Acute flaccid myelitis; AFM; Polio-like syndrome; Acute flaccid paralysis; Acute flaccid paralysis with anterior myelitis; Anterior myelitis; Enterovirus D68; Enterovirus A71Acute flaccid myelitis (AFM) is a rare condition that affects the nervous system. Inflammation of the gray matter in the spinal cord leads to muscle weakness and paralysis.
AFM is usually caused by an infection with a virus. While AFM is rare, there has been a slight increase in cases of AFM since 2014. Most new cases have occurred in children or young adults.
Causes
AFM usually occurs after a cold, fever, or gastrointestinal illness.
Cold
The common cold most often causes a runny nose, nasal congestion, and sneezing. You may also have a sore throat, cough, headache, or other symptoms....

Different kinds of viruses may be the cause of AFM. These include:
- Enteroviruses (poliovirus and non-poliovirus)
Poliovirus
Polio is a viral disease that can affect nerves and can lead to partial or full paralysis. The medical name for polio is poliomyelitis.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
West Nile virus and similar viruses such as Japanese encephalitis virus and Saint Louis encephalitis virus
West Nile virus
West Nile virus causes a viral disease and is spread by mosquitoes. The condition ranges from mild to severe.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Adenoviruses
It is unclear why certain viruses trigger AFM, or why some people develop the condition and others don't.
Environmental toxins also can cause AFM. In many cases, a cause is never found.
Symptoms
A fever or a respiratory illness is often present before weakness and other symptoms begin.
AFM symptoms often start with sudden muscle weakness and loss of reflexes in an arm or leg. Symptoms may progress rapidly over a few hours to days. Other symptoms may include:
- Facial droop or weakness
-
Drooping eyelids
Drooping eyelids
Eyelid drooping is excess sagging of the upper eyelid. The edge of the upper eyelid may be lower than it should be (ptosis) or there may be excess b...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Difficulty moving the eyes
-
Slurred speech or difficulty swallowing
Slurred speech
Dysarthria is a condition in which you have difficulty saying words because of problems with the muscles that help you talk.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleDifficulty swallowing
Difficulty with swallowing is the feeling that food or liquid is stuck in the throat or at any point before the food enters the stomach. This proble...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Some people may have:
- Stiffness in the neck
- Pain in the arms or legs
- Inability to pass urine
Severe symptoms include:
- Respiratory failure, when muscles involved in breathing become weak
- Serious nervous system problems, which may lead to death
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will take your medical history and vaccination history to know if you are up-to-date with your polio vaccines. Unvaccinated individuals who are exposed to poliovirus are at higher risk for AFM. Your provider also may want to know if within the last 4 weeks you have:
- Traveled
- Had a cold or the flu or a stomach bug
- Had a fever 100°F (37.8°C) or higher
Your provider will do a physical exam. Tests that may be done include:
-
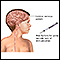
MRI of spine and MRI of the brain to view lesions in the gray matter
MRI of spine
A cervical MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scan uses energy from strong magnets to create pictures of the part of the spine that runs through the ne...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleMRI of the brain
A head MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the brain and surrounding...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
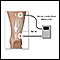
Nerve conduction velocity test
Nerve conduction velocity test
Nerve conduction velocity (NCV) is a test to see how fast electrical signals move through a nerve. This test is done along with electromyography (EM...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
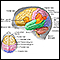
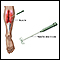
Electromyography (EMG)
Electromyography (EMG)
Electromyography (EMG) is a test that checks the health of the muscles and the nerves that control the muscles.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
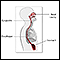
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis to check if white blood cells are elevated
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis is a group of lab tests that measure chemicals in the cerebrospinal fluid. CSF is a clear fluid that surrounds an...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Your provider also may take stool, blood, and saliva samples to test.
Treatment
There is no specific treatment for AFM. You may be referred to a doctor specializing in disorders of the nerves and nervous system (neurologist). The neurologist will likely help treat your symptoms.
A number of medicines and treatments that work on the immune system have been tried but have not been found to help.
You may need physical therapy to help restore muscle function.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The long-term outlook of AFM is not known.
Possible Complications
Complications of AFM include:
- Muscle weakness and paralysis
- Loss of limb function
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider right away if you or your child have:
- Sudden weakness in the arms or legs or difficulty moving the head or face
- Any other symptom of AFM
Prevention
There is no known way to prevent AFM. Having a polio vaccine may help reduce the risk of AFM related to the poliovirus.
Polio vaccine
All content below is taken in its entirety from the CDC Polio Vaccine Information Statement (VIS): www. cdc. gov/vaccines/hcp/current-vis/polio. html...
Take these steps to help avoid viral infections:
- Wash hands frequently with soap and water, especially before eating.
- Avoid close contact with people who have a viral infection.
- Use mosquito repellants when going outdoors to prevent mosquito bites.
To learn more and get recent updates, go to the CDC webpage about AFM at www.cdc.gov/acute-flaccid-myelitis/index.html.
References
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. Acute flaccid myelitis (AFM). www.cdc.gov/acute-flaccid-myelitis/index.html. Updated May 9, 2024. Accessed November 8, 2024.
Kapadia RK, Pastula DM, Glaser CA. Parainfectious and postinfectious neurologic syndromes. In: Long SS, Prober CG, Fischer M, Kimberlin DW, eds. Principles and Practice of Pediatric Infectious Diseases. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 45.
Messacar K, Abzug MJ. Enteroviruses and parechoviruses. In: Long SS, Prober CG, Fischer M, Kimberlin DW, eds. Principles and Practice of Pediatric Infectious Diseases. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 236.
-
MRI scans - illustration
MRI stands for magnetic resonance imaging. It allows imaging of the interior of the body without using x-rays or other types of ionizing radiation. An MRI scan is capable of showing fine detail of different tissues.
MRI scans
illustration
-
CSF chemistry - illustration
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear fluid that circulates in the space surrounding the spinal cord and brain. CSF protects the brain and spinal cord from injury by acting like a liquid cushion. CSF is usually obtained through a lumbar puncture (spinal tap). During the procedure, a needle is inserted usually between the third and fourth lumbar vertebrae and the CSF fluid is collected for testing.
CSF chemistry
illustration
-
Electromyography - illustration
Electromyography is a test that measures muscle response to nervous stimulation. A needle electrode is inserted through the skin into the muscle. Each muscle fiber that contracts will produce an action potential. The presence, size, and shape of the wave form of the action potential produced on the oscilloscope, provides information about the ability of the muscle to respond to nervous stimulation.
Electromyography
illustration
-
MRI scans - illustration
MRI stands for magnetic resonance imaging. It allows imaging of the interior of the body without using x-rays or other types of ionizing radiation. An MRI scan is capable of showing fine detail of different tissues.
MRI scans
illustration
-
CSF chemistry - illustration
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear fluid that circulates in the space surrounding the spinal cord and brain. CSF protects the brain and spinal cord from injury by acting like a liquid cushion. CSF is usually obtained through a lumbar puncture (spinal tap). During the procedure, a needle is inserted usually between the third and fourth lumbar vertebrae and the CSF fluid is collected for testing.
CSF chemistry
illustration
-
Electromyography - illustration
Electromyography is a test that measures muscle response to nervous stimulation. A needle electrode is inserted through the skin into the muscle. Each muscle fiber that contracts will produce an action potential. The presence, size, and shape of the wave form of the action potential produced on the oscilloscope, provides information about the ability of the muscle to respond to nervous stimulation.
Electromyography
illustration
Review Date: 10/23/2024
Reviewed By: Joseph V. Campellone, MD, Department of Neurology, Cooper Medical School at Rowan University, Camden, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.