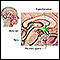
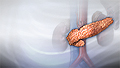
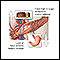
Endocrine glands
Endocrine glands release (secrete) hormones into the bloodstream.
The endocrine glands include the:
- Adrenal
- Hypothalamus
- Islets of Langerhans in the pancreas
- Ovaries
- Parathyroid
- Pineal
- Pituitary
- Testes
- Thyroid
-
Information
Hypersecretion is when an excess of one or more hormone is secreted from a gland. Hyposecretion is when the amount of hormones that are released is too low.
There are many types of disorders that can result when too much or too little of a hormone is released.
Disorders that may be associated with abnormal hormone product from a particular gland include:
Adrenal:
- Addison disease
- Adrenogenital syndrome or adrenocortical hyperplasia
- Cushing syndrome
- Pheochromocytoma
Pancreas:
Parathyroid:
- Low or high blood calcium level
- Tetany (abnormal cramping of muscles)
- Renal calculi (kidney stones)
- Excessive loss of minerals from bone (osteoporosis)
Pituitary:
- Growth hormone deficiency
- Acromegaly
- Gigantism
- Diabetes insipidus
- Cushing disease
Testes and ovaries:
- Lack of sex development (unclear genitalia)
Thyroid:
- Congenital hypothyroidism
- Myxedema
- Goiter
- Thyrotoxicosis
References
Clemmons DR, Nieman LK. Approach to the patient with endocrine disease. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 202.
Jameson JL. Principles of endocrinology. In: Robertson RP, ed. DeGroot's Endocrinology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 1.
Melmed S, Auchus RJ, Goldfine AB, Kopp PA, Rosen CJ, et al. Principles of endocrinology. In: Melmed S, Auchus RJ, Goldfine AB, Rosen CJ, Kopp PA, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. 15th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 1.